이번에는 지금까지 만들어온 일명 CelebA GAN을 기반으로, 다음 두 가지 문제를 중심적으로 해결하는 모델을 만들어보겠다.
1. 이미지가 약간 불명확하다. 부드럽게 이어져 있어야 할 공간들이 고대비 픽셀로 채워져 있다.
2. 완전 연결 신경망은 꽤 많은 메모리를 사용한다. 어느 정도 큰 이미지를 대상으로 훈련한다면 GPU의 한계를 넘어서서 훈련이 어려울 수 있다.
- 판별기 네트워크
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
# initialise parent pytorch class
super().__init__()
# define neural network layers
self.model = nn.Sequential(
# expect input of shape (1,3,128,128)
nn.Conv2d(3, 256, kernel_size=8, stride=2),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=8, stride=2),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.Conv2d(256, 3, kernel_size=8, stride=2),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
View(3*10*10),
nn.Linear(3*10*10, 1),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
# create loss function
self.loss_function = nn.BCELoss()
# create optimiser, simple stochastic gradient descent
self.optimiser = torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
# counter and accumulator for progress
self.counter = 0;
self.progress = []
pass
def forward(self, inputs):
# simply run model
return self.model(inputs)
def train(self, inputs, targets):
# calculate the output of the network
outputs = self.forward(inputs)
# calculate loss
loss = self.loss_function(outputs, targets)
# increase counter and accumulate error every 10
self.counter += 1;
if (self.counter % 10 == 0):
self.progress.append(loss.item())
pass
if (self.counter % 1000 == 0):
print("counter = ", self.counter)
pass
# zero gradients, perform a backward pass, update weights
self.optimiser.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimiser.step()
pass
def plot_progress(self):
df = pandas.DataFrame(self.progress, columns=['loss'])
df.plot(ylim=(0), figsize=(16,8), alpha=0.1, marker='.', grid=True, yticks=(0, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, 5.0))
pass
pass
- 생성기 네트워크
여기서는 전치 합성곱(transposed convolution)이 사용된다.
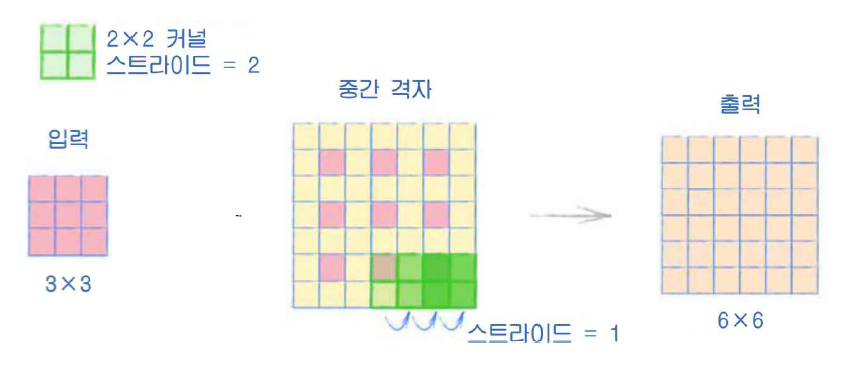
출력 값의 공식은 커널 사이즈 + (스트라이드 * 입력 사이즈 -1) + 패딩이다.
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
# initialise parent pytorch class
super().__init__()
# define neural network layers
self.model = nn.Sequential(
# input is a 1d array
nn.Linear(100, 3*11*11),
#nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.GELU(),
# reshape to 4d
View((1, 3, 11, 11)),
nn.ConvTranspose2d(3, 256, kernel_size=8, stride=2),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
#nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.GELU(),
nn.ConvTranspose2d(256, 256, kernel_size=8, stride=2),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
#nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.GELU(),
nn.ConvTranspose2d(256, 3, kernel_size=8, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(3),
# output should be (1,3,128,128)
nn.Sigmoid()
)
# create optimiser, simple stochastic gradient descent
self.optimiser = torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
# counter and accumulator for progress
self.counter = 0;
self.progress = []
pass
def forward(self, inputs):
# simply run model
return self.model(inputs)
def train(self, D, inputs, targets):
# calculate the output of the network
g_output = self.forward(inputs)
# pass onto Discriminator
d_output = D.forward(g_output)
# calculate error
loss = D.loss_function(d_output, targets)
# increase counter and accumulate error every 10
self.counter += 1;
if (self.counter % 10 == 0):
self.progress.append(loss.item())
pass
# zero gradients, perform a backward pass, update weights
self.optimiser.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimiser.step()
pass
def plot_progress(self):
df = pandas.DataFrame(self.progress, columns=['loss'])
df.plot(ylim=(0), figsize=(16,8), alpha=0.1, marker='.', grid=True, yticks=(0, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, 5.0))
pass
pass
'GAN > 이론' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 9. MSE 손실, BCE 손실 (0) | 2021.11.08 |
|---|---|
| 8. 조건부 GAN (0) | 2021.11.08 |
| 6. 얼굴 이미지(HDF5 데이터 형식, GPU 가속) (0) | 2021.11.06 |
| 5. 손으로 쓴 숫자 훈련(2) (0) | 2021.11.03 |
| 4. 손으로 쓴 숫자 훈련 (1) (0) | 2021.11.03 |