이번 포스팅에서는 자동차 번호판의 글씨를 인식하는 프로젝트에 대해서 정리하겠다.
프로젝트 진행 과정은 다음과 같다.
1. yolo를 사용해 이미지 내에서 자동차를 찾는다.
2. 자동차만 나오게 만들어준 사진에서 번호판을 찾는다.(EAST detector 사용)
3. pytesseract 모듈을 사용해 글씨를 인식한다.
먼저 필요한 모듈을 import하고 yolo를 load한다.
import cv2
import numpy as np
from imutils.object_detection import non_max_suppression
import pytesseract
min_confidence = 0.5
file_name = "image/image_03.png"
east_decorator = 'frozen_east_text_detection.pb'
frame_size = 320
padding = 0.05
# Load Yolo
net = cv2.dnn.readNet("yolo/yolov3.weights", "yolo/yolov3.cfg")
layer_names = net.getLayerNames()
output_layers = [layer_names[i[0] - 1] for i in net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()]
yolo를 통해 자동차를 찾아내는 코드이다. 앞선 포스팅에서 다루었던 내용이다.
def carROI(image):
height, width, channels = image.shape
# Detecting objects
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(img, 0.00392, (416, 416), (0, 0, 0), True, crop=False)
net.setInput(blob)
outs = net.forward(output_layers)
# Showing informations on the screen
confidences = []
boxes = []
img_cars = []
for out in outs: # 객체들
for detection in out: # 객체 하나를 둘러싼 box들
scores = detection[5:]
class_id = np.argmax(scores)
confidence = scores[class_id]
# Filter only 'car'
if class_id == 2 and confidence > min_confidence:
# Object detected
center_x = int(detection[0] * width)
center_y = int(detection[1] * height)
w = int(detection[2] * width)
h = int(detection[3] * height)
# Rectangle coordinates
x = int(center_x - w / 2)
y = int(center_y - h / 2)
boxes.append([x, y, w, h])
confidences.append(float(confidence))
indexes = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, min_confidence, 0.4) # 제일 좋은 box의 index를 리턴
for i in range(len(boxes)):
if i in indexes:
x, y, w, h = boxes[i]
img_cars.append(image[y:y+h, x:x+w])
return (boxes[i], image[y:y+h, x:x+w]) # 최종 box의 좌표와 car image부분만 잘라서 리턴
다음은 자동차 이미지에서 EAST detector를 사용해 번호판을 찾아내는 코드이다.
def textROI(image):
# load the input image and grab the image dimensions
orig = image.copy()
(origH, origW) = image.shape[:2]
# 자동차 이미지를 잘라오게 되면 자동차의 크기에 따라 이미지의 사이즈가 달라지기 때문에(정사각형이 아니기 때문에)
# 번호판 글씨가 왜곡(늘려지거나 줄여지는 현상)될 수 있다(번호판은 차의 중앙에 있다)
# 그러므로 늘리거나 줄임없이 정사각형 이미지로(320x320) 잘라내기 위해 다음 작업을 실행한다.
rW = origW / float(frame_size)
rH = origH / float(frame_size)
newW = int(origW / rH)
center = int(newW / 2)
start = center - int(frame_size / 2)
# resize the image and grab the new image dimensions
image = cv2.resize(image, (newW, frame_size))
scale_image = image[0:frame_size, start:start+frame_size]
(H, W) = scale_image.shape[:2]
cv2.imshow("orig", orig)
cv2.imshow("resize", image)
cv2.imshow("scale_image", scale_image)
# define the two output layer names for the EAST detector model
layerNames = [
"feature_fusion/Conv_7/Sigmoid",
"feature_fusion/concat_3"]
# load the pre-trained EAST text detector
net = cv2.dnn.readNet(east_decorator)
# construct a blob from the image
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(image, 1.0, (frame_size, frame_size),
(123.68, 116.78, 103.94), swapRB=True, crop=False)
net.setInput(blob)
(scores, geometry) = net.forward(layerNames)
(numRows, numCols) = scores.shape[2:4]
rects = []
confidences = []
# loop over the number of rows
for y in range(0, numRows):
# extract the scores (probabilities)
scoresData = scores[0, 0, y]
xData0 = geometry[0, 0, y]
xData1 = geometry[0, 1, y]
xData2 = geometry[0, 2, y]
xData3 = geometry[0, 3, y]
anglesData = geometry[0, 4, y]
# loop over the number of columns
for x in range(0, numCols):
if scoresData[x] < min_confidence:
continue
(offsetX, offsetY) = (x * 4.0, y * 4.0)
angle = anglesData[x]
cos = np.cos(angle)
sin = np.sin(angle)
h = xData0[x] + xData2[x]
w = xData1[x] + xData3[x]
endX = int(offsetX + (cos * xData1[x]) + (sin * xData2[x]))
endY = int(offsetY - (sin * xData1[x]) + (cos * xData2[x]))
startX = int(endX - w)
startY = int(endY - h)
rects.append((startX, startY, endX, endY))
confidences.append(scoresData[x])
# apply non-maxima suppression
boxes = non_max_suppression(np.array(rects), probs=confidences)
# initialize the list of results
results = []
# loop over the bounding boxes
for (startX, startY, endX, endY) in boxes:
startX = int(startX * rW)
startY = int(startY * rH)
endX = int(endX * rW)
endY = int(endY * rH)
dX = int((endX - startX) * padding)
dY = int((endY - startY) * padding)
startX = max(0, startX - dX)
startY = max(0, startY - dY)
endX = min(origW, endX + (dX * 2))
endY = min(origH, endY + (dY * 2))
# extract the actual padded ROI
return ([startX, startY, endX, endY], orig[startY:endY, startX:endX])

다음은 테서렉트를 이용한 글씨 인식 코드이다.
def textRead(image):
# apply Tesseract v4 to OCR
config = ("-l eng --oem 1 --psm 7")
text = pytesseract.image_to_string(image, config=config)
# display the text OCR'd by Tesseract
print("OCR TEXT : {}\n".format(text))
# strip out non-ASCII text
text = "".join([c if c.isalnum() else "" for c in text]).strip()
print("Alpha numeric TEXT : {}\n".format(text))
return text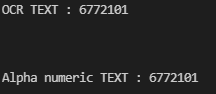
아쉽게도 내가 준비한 이미지에서는 Z와 2,7을 잘 구분해내지 못했다.
마지막으로 main함수 부분이다.
# Loading image
img=cv2.imread(file_name)
img_copy=img.copy()
([x,y,w,h],car_image) = carROI(img)
([startX,startY,endX,endY], text_image) = textROI(car_image)
process_image = processROI(text_image)
text = textRead(process_image)
cv2.rectangle(img_copy, (x+startX, y+startY), (x+endX, y+endY), (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(img_copy, text, (x+startX, y+startY-10),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1.2, (0, 0, 255), 3)
# show the output image
cv2.imshow("OCR Text Recognition : "+text, img_copy)
cv2.imshow('plate_img',text_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
참고:
https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2018/08/20/opencv-text-detection-east-text-detector
'Object Detection' 카테고리의 다른 글
| tesseract와 EAST detector를 이용한 글씨 인식 (0) | 2021.09.05 |
|---|---|
| 직접 쓴 손 글씨(숫자) 인식하기 - 글씨 추출 및 검출 (0) | 2021.08.27 |
| 직접 쓴 손 글씨(숫자) 인식하기 - 필터링을 통한 인식률 향상시키는 방법 (0) | 2021.08.26 |
| object detection project - keras를 사용한 detection(2) (0) | 2021.08.26 |
| object detection project - keras를 사용한 detection(1) (0) | 2021.08.24 |