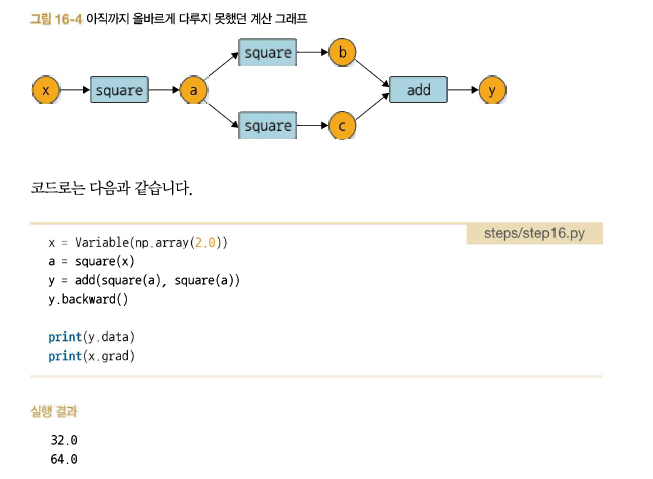
지금의 DeZero는 다음 그림과 같은 계산 그래프도 만들 수 있다.
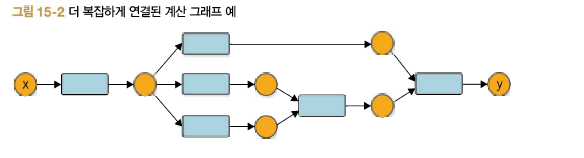
그러나 지금의 DeZero는 이런 계산의 미분은 제대로 계산하지 못한다. 더 정확하게는 이런 복잡한 연결의 역전파를 제대로 할 수 없다.
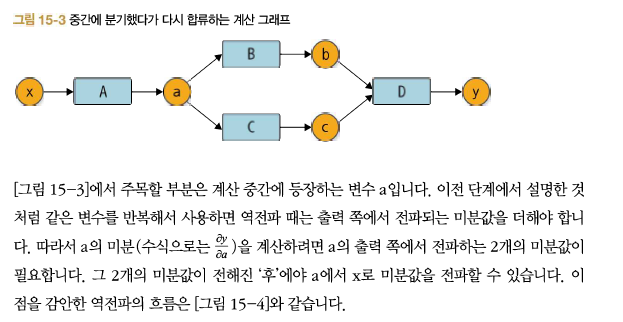
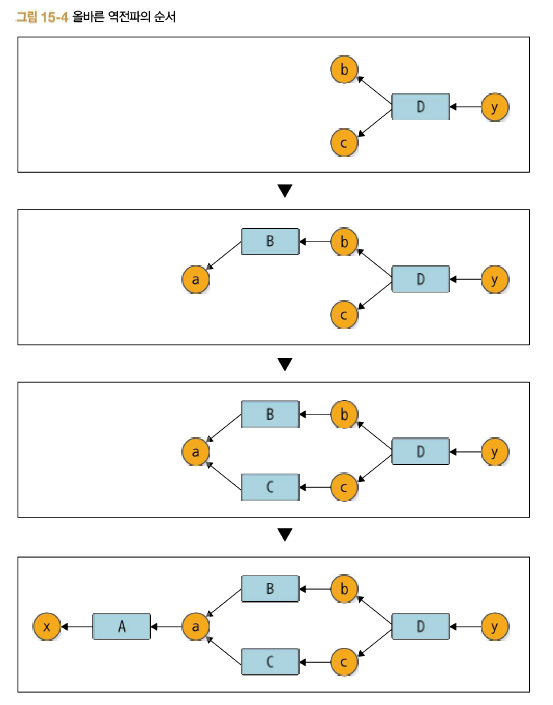
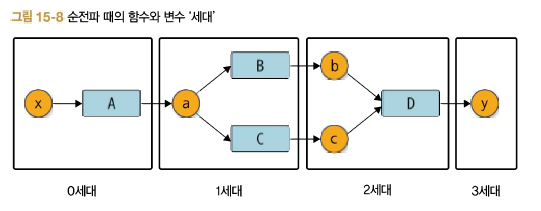
- 세대 추가
class Variable: def __init__(self,data): if data is not None: if not isinstance(data,np.ndarray): raise TypeError('{}는 지원하지 않습니다'.format(type(data))) self.data=data self.grad=None self.creator=None self.generation=0 # 세대 수를 기록하는 변수 def set_creator(self,func): self.creator=func self.generation=func.generation + 1 def backward(self): if self.grad is None: self.grad = np.ones_like(self.data) funcs=[self.creator] while funcs: f=funcs.pop() gys=[output.grad for output in f.outputs] gxs=f.backward(*gys) if not isinstance(gxs,tuple): gxs=(gxs,) for x,gx in zip(f.inputs,gxs): if x.grad is None: x.grad=gx else: x.grad=x.grad + gx if x.creator is not None: funcs.append(x.creator) def cleargrad(self): self.grad=None
Variable 클래스는 generation을 0으로 초기화한다. 그리고 set_creator 메서드가 호출될 때 부모 함수의 새대보다 1만큼 큰 값을 설정한다.

다음 차례는 Functoin클래스이다. Function클래스의 generation은 입력 변수와 같은 값으로 설정한다.
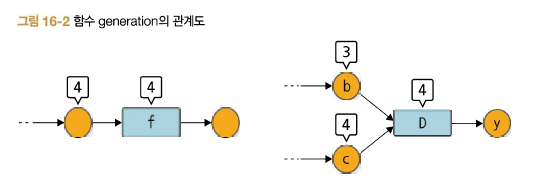
입력 변수가 둘 이상이라면 가장 큰 generation의 수를 선택한다.
class Function:
def __call__(self, *inputs):
xs=[x.data for x in inputs]
ys=self.forward(*xs)
if not isinstance(ys,tuple):
ys=(ys,)
outputs=[Variable(as_array(y)) for y in ys]
self.generation=max([x.generation for x in inputs])
for output in outputs:
output.set_creator(self) # 출력 변수에 참조자 설정
self.inputs=inputs
self.outputs=outputs # 출력도 저장 [6]
return outputs if len(outputs)> 1 else outputs[0]
def forward(self,xs):
raise NotImplementedError()
def backward(self,gys):
raise NotImplementedError()
- 세대 순으로 꺼내기
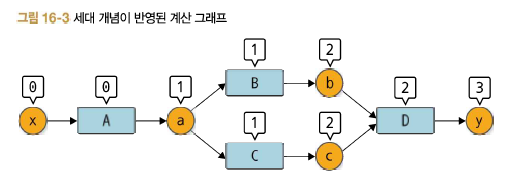
이렇게 세대가 설정되어 있으면 역전파 때 함수를 올바른 순서로 꺼낼 수 있다. 예를 들어 함수 A보다 세대가 큰 B와 C를 먼저 꺼내게 된다.

- Variable 클래스의 backward
class Variable: def __init__(self,data): if data is not None: if not isinstance(data,np.ndarray): raise TypeError('{}는 지원하지 않습니다'.format(type(data))) self.data=data self.grad=None self.creator=None self.generation=0 # 세대 수를 기록하는 변수 def set_creator(self,func): self.creator=func self.generation=func.generation + 1 def backward(self): if self.grad is None: self.grad = np.ones_like(self.data) funcs=[] seen_set=set() def add_func(f): if f not in seen_set: funcs.append(f) seen_set.add(f) funcs.sort(key=lambda x: x.generation) add_func(self.creator) while funcs: f=funcs.pop() gys=[output.grad for output in f.outputs] gxs=f.backward(*gys) if not isinstance(gxs,tuple): gxs=(gxs,) for x,gx in zip(f.inputs,gxs): if x.grad is None: x.grad=gx else: x.grad=x.grad + gx if x.creator is not None: add_func(x.creator) def cleargrad(self): self.grad=None

'Deep learning > 모델 구현' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 28. 변수 사용성 개선 (0) | 2021.10.10 |
|---|---|
| 27. 메모리 관리 (0) | 2021.10.04 |
| 25. 가변 길이 인수(역전파) (0) | 2021.10.04 |
| 24. 가변 길이 인수(순전파) (0) | 2021.10.04 |
| 23. 역전파 자동화 (0) | 2021.09.29 |