이번 포스팅에서는 yolov3를 이용해 object detection을 하는 방법에 대해 정리해보겠다. 여기서는 사전학습된 weights 를 가지고 객체탐지를 실행했다. 코드 설명은 주석마다 잘 설명해놓았다.
1. 이미지 객체 인식
import cv2
import numpy as np
min_confidence=0.5
# Load yolo
net=cv2.dnn.readNet('yolov3.weights','yolov3.cfg')
classes=[]
with open('coco.names','r') as f: # 파일을 읽어와 f에 두고
classes=[line.strip() for line in f.readlines()] # 이름 파일의 이름들이 배열에 들어감
# yolo의 작동 방식
layer_names=net.getLayerNames()
output_layers=[layer_names[i[0]-1] for i in net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()]
colors=np.random.uniform(0,255,size=(len(classes),3)) # 각각의 클래스들의 색을 다르게 표현
#Loading image
img=cv2.imread('image_01.jpg')
#img=cv2.resize(img,None,fx=0.4,fy=0.4) #사이즈를 0.4만큼 줄임
height,width,channels = img.shape
cv2.imshow('Original image',img)
#Detecting objects
#(416,416) 사이즈로 이미지를 만들어준다. -> 스피드와 정확도가 둘다 적당하다.
blob=cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(img,1/255.,(416,416),(0,0,0),True,crop=False)
net.setInput(blob)
outs=net.forward(output_layers) #어던 물체를 detect했는지에 대한 정보가 들어있다.
# Showing informations on the screen
class_ids=[]
confidences=[]
boxes=[]
for out in outs:
for detection in out:
scores=detection[5:]
class_id=np.argmax(scores)
confidence=scores[class_id]
if confidence>min_confidence:
# Object detected
center_x=int(detection[0] * width)
center_y=int(detection[1] * height)
w=int(detection[2] * width)
h=int(detection[3] * height)
# Rectangle coordinates
x=int(center_x - w / 2)
y=int(center_y - h / 2)
boxes.append([x,y,w,h])
confidences.append(float(confidence))
class_ids.append(class_id)
indexes=cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes,confidences,min_confidence,0.4)
# 여러개의 박스가 생기는데 이중 하나의 박스로 줄여준다.min_confidence=> confidence의 임계값 0.4=>NMS의 임계값, boxes안에 몇번째 box가 유의미 한지 인덱스 넘겨줌
font=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN
for i in range(len(boxes)): #모든 boxes중 NMS에 의해 기록된 유의미한 인덱스만 골라내기 위한 과정
if i in indexes: # 유의미한 인덱스가 걸리게 되면
x,y,w,h=boxes[i] # 유의미한 box
label=str(classes[class_ids[i]]) #classes[index of class]
print(i,label)
color=colors[i]
cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),color,2)
cv2.putText(img,label,(x,y),font,2,(0,255,0),1)
cv2.imshow('image',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()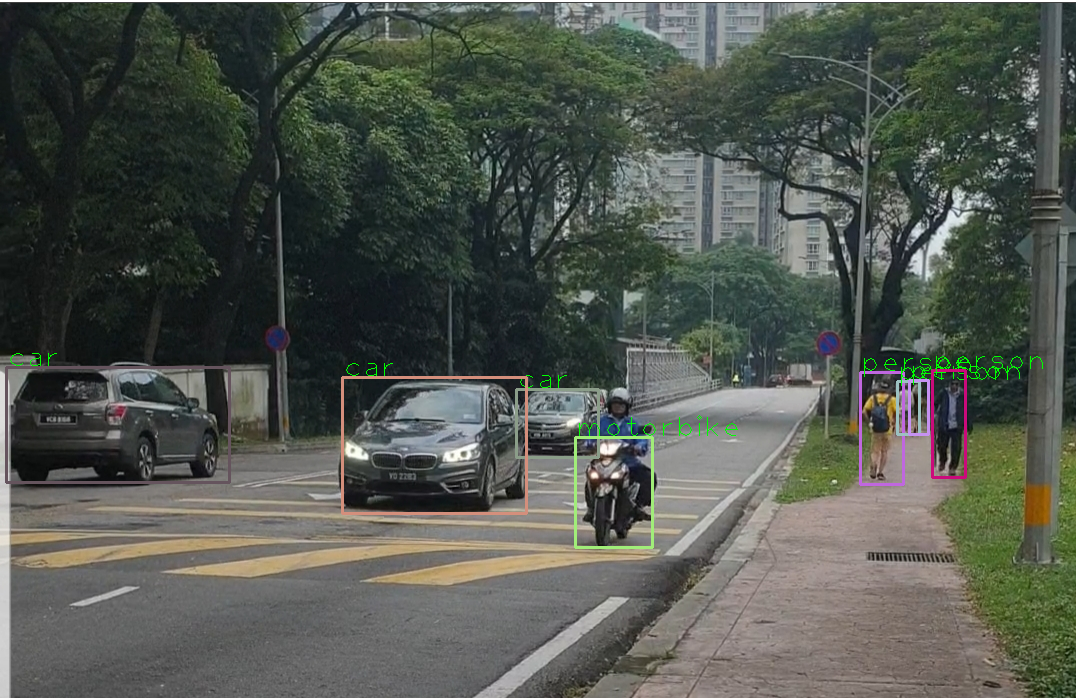
2. 동영상 객체 인식
이미지 인식때 사용했던 main code들을 함수화 시켰다. 영상을 불러와야 하기 때문에 이렇게 처리하는 편이 더 깔끔하다.
import cv2
import numpy as np
import time
file_name='video_01.mp4'
min_confidence=0.5
def detectAndDisplay(frame):
start_time=time.time()
img=cv2.resize(frame,None,fx=0.4,fy=0.4) #사이즈를 0.4만큼 줄임
height,width,channels = img.shape
cv2.imshow('Original image',img)
#Detecting objects
#(416,416) 사이즈로 이미지를 만들어준다. -> 스피드와 정확도가 둘다 적당하다.
blob=cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(img,1/255.,(416,416),(0,0,0),True,crop=False)
net.setInput(blob)
outs=net.forward(output_layers) #어던 물체를 detect했는지에 대한 정보가 들어있다.
# Showing informations on the screen
class_ids=[]
confidences=[]
boxes=[]
for out in outs:
for detection in out:
scores=detection[5:]
class_id=np.argmax(scores)
confidence=scores[class_id]
if confidence>min_confidence:
# Object detected
center_x=int(detection[0] * width)
center_y=int(detection[1] * height)
w=int(detection[2] * width)
h=int(detection[3] * height)
# Rectangle coordinates
x=int(center_x - w / 2)
y=int(center_y - h / 2)
boxes.append([x,y,w,h])
confidences.append(float(confidence))
class_ids.append(class_id)
indexes=cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes,confidences,min_confidence,0.4)
# 여러개의 박스가 생기는데 이중 하나의 박스로 줄여준다.min_confidence=> confidence의 임계값 0.4=>NMS의 임계값, boxes안에 몇번째 box가 유의미 한지 인덱스 넘겨줌
font=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN
for i in range(len(boxes)): #모든 boxes중 NMS에 의해 기록된 유의미한 인덱스만 골라내기 위한 과정
if i in indexes: # 유의미한 인덱스가 걸리게 되면
x,y,w,h=boxes[i] # 유의미한 box
# 이름과 몇퍼센트 확률인지 보여준다.
label='{}: {:.2f}'.format(classes[class_ids[i]],confidences[i] * 100) #classes[index of class]
print(i,label)
color=colors[i]
cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),color,2)
cv2.putText(img,label,(x,y-5),font,1,color,1)
end_time=time.time()
process_time=end_time - start_time
print('A frame took {:.3f} seconds'.format(process_time))
cv2.imshow('YOLO image',img)
# Load yolo
net=cv2.dnn.readNet('yolov3.weights','yolov3.cfg')
classes=[]
with open('coco.names','r') as f: # 파일을 읽어와 f에 두고
classes=[line.strip() for line in f.readlines()] # 이름 파일의 이름들이 배열에 들어감
# yolo의 작동 방식
layer_names=net.getLayerNames()
output_layers=[layer_names[i[0]-1] for i in net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()]
colors=np.random.uniform(0,255,size=(len(classes),3)) # 각각의 클래스들의 색을 다르게 표현
# Read the video stream
cap=cv2.VideoCapture(file_name)
if not cap.isOpened:
print('--ERROR opening video capture')
exit(0)
while True:
ret,frame=cap.read()
if frame is None:
print('! No captured frame --Break!')
break
detectAndDisplay(frame)
# hit 'g' on the keyboard to quit!
if cv2.waitKey(1)==27:
break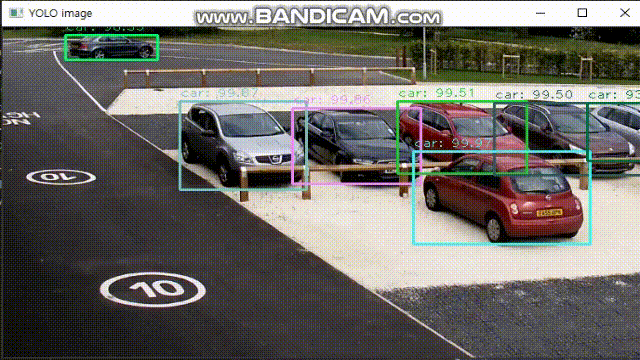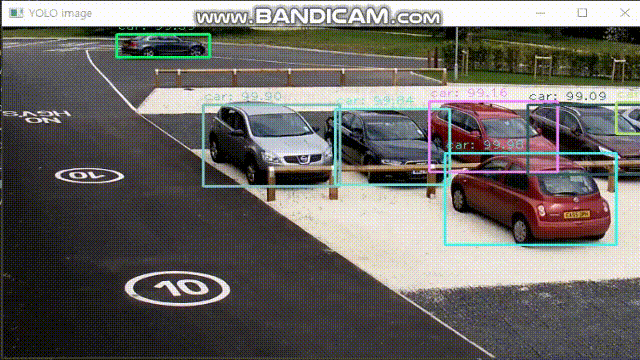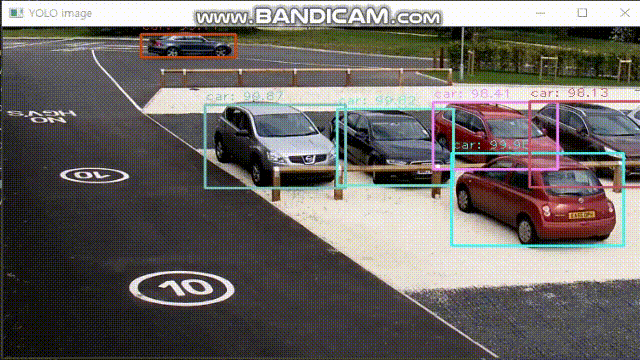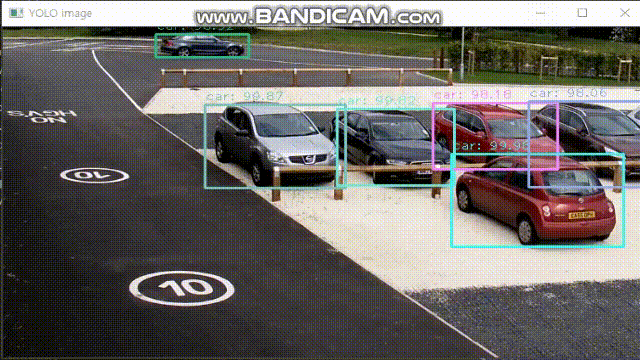
'Object Detection' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Custom YOLO project - 대용량 xml파일 라벨링 해주기 (0) | 2021.08.21 |
|---|---|
| Custom YOLO project - YOLO 이미지 데이터 만들기 (0) | 2021.08.21 |
| 졸음 감지 프로젝트 (0) | 2021.08.16 |
| face_aligned_photo_generator (0) | 2021.08.16 |
| face alignment (0) | 2021.08.15 |